NEWS AND EVENTS
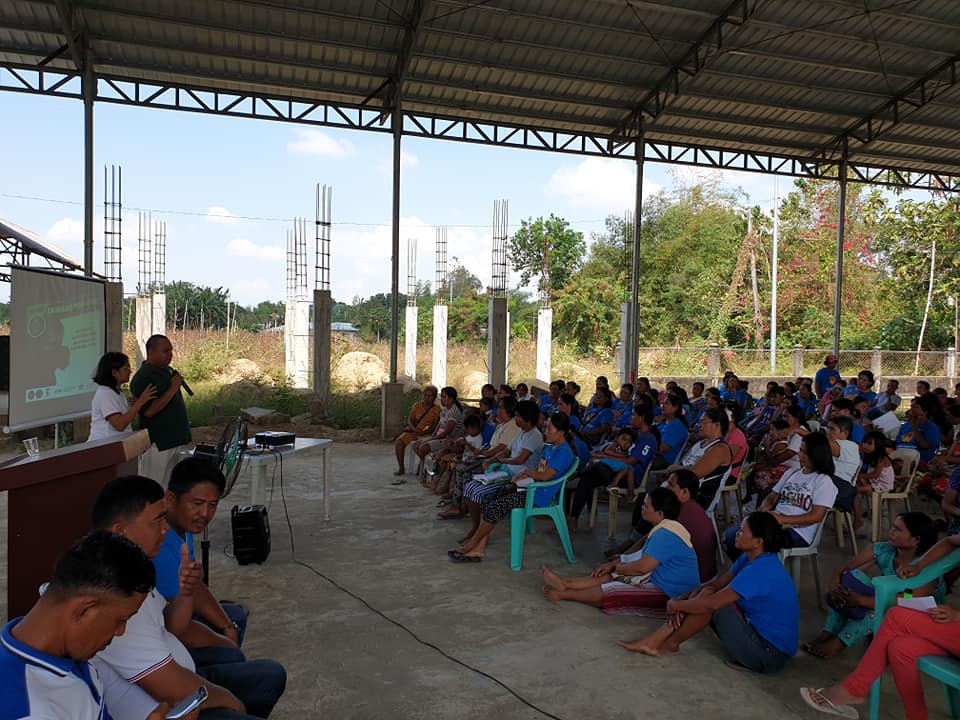


Hermano at Hermana Mayor, BMCCA, Nagpulong pa..
12/10/23 | Tourism
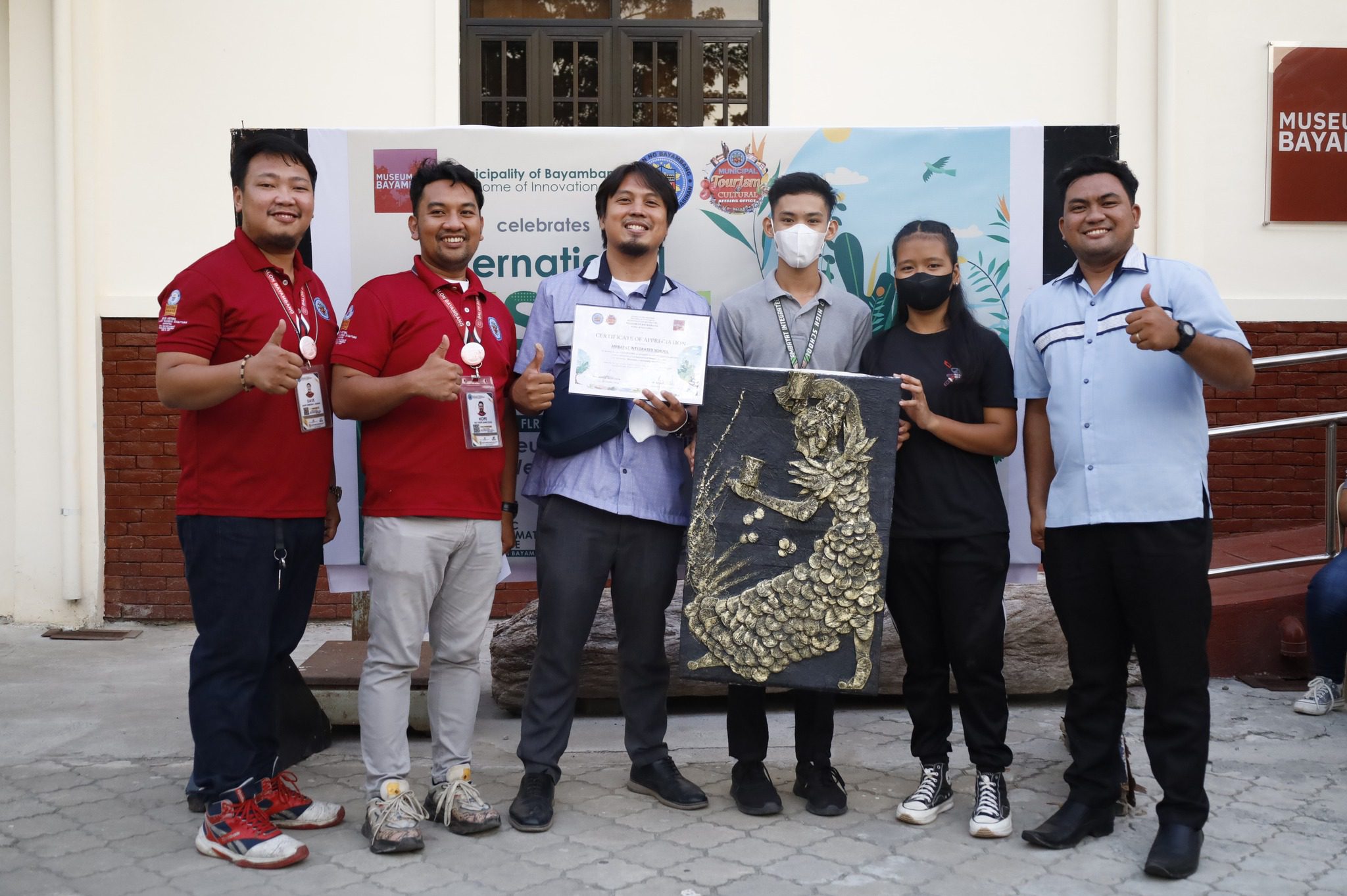

International Museum Day 2023, Ipinagdiwang!
08/14/23 | Tourism
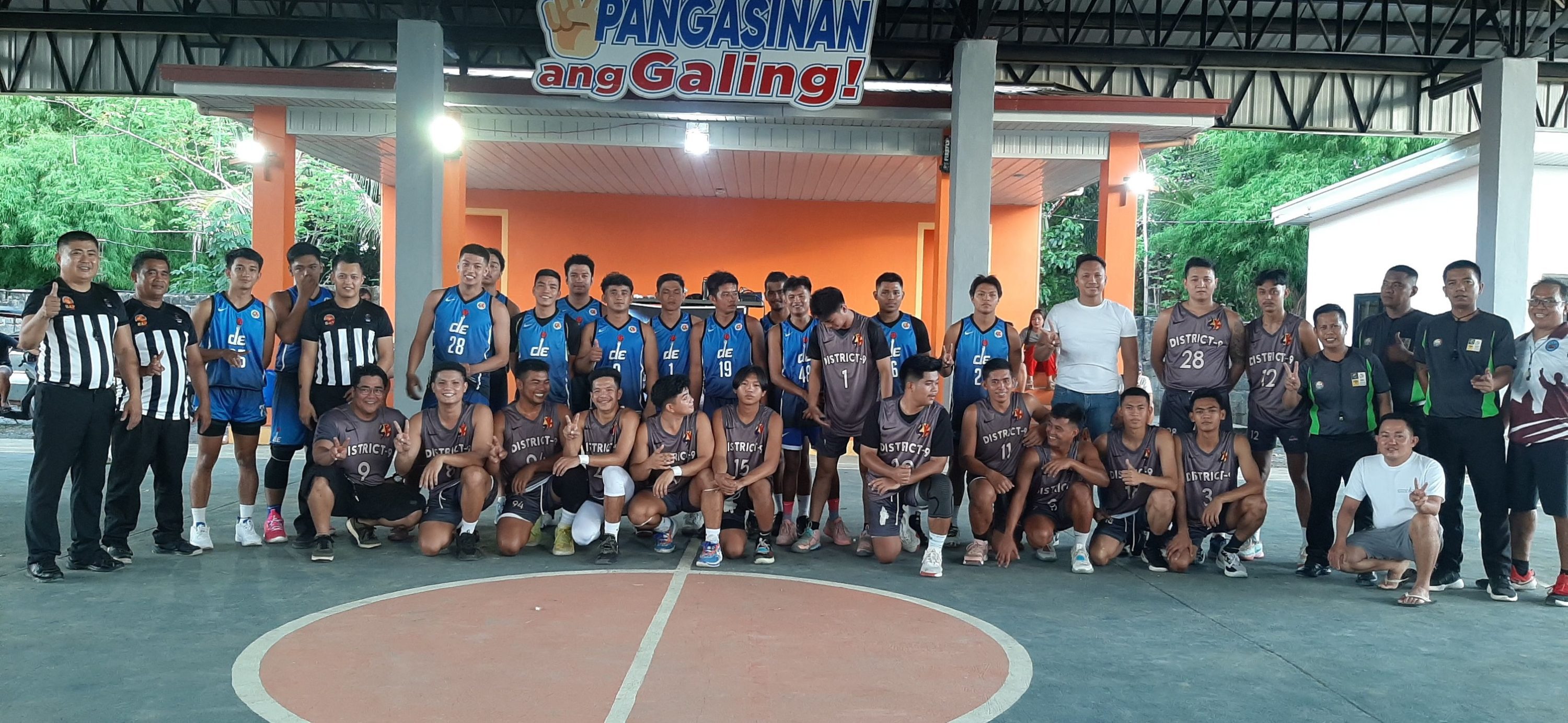

UPDATE | LGU Bayambang Inter-District Basketb..
08/14/23 | Sports

VM IC Sabangan, Panauhing Pandangal sa IBP Re..
08/14/23 | Social Services

2Q MAC Meeting | MNJQ, Nangakong Dodoblehin a..
08/14/23 | Social Services

Joint Blood Drive with Lecture Demo on First ..
08/14/23 | Social Services











 Business
Business People
People Tourism
Tourism


 Executive Orders
Executive Orders Ordinances
Ordinances Bids and Awards
Bids and Awards